The recent Fed rate cut marks a pivotal moment in the financial landscape, as the Federal Reserve moves to lower borrowing costs for consumers and businesses alike. This significant reduction is poised to have ripple effects across various sectors, notably influencing mortgage rates, which are expected to decline as the Fed eases monetary policy. Economists predict that the economic impact of rate cuts will be felt widely, stimulating consumer borrowing and spending while providing much-needed relief for those struggling with high interest rates. As interest rate predictions remain optimistic, stakeholders are keenly observing how these changes will affect their financial commitments. With the Fed’s decision, many anticipate a gradual improvement in the economy that will help bolster both Wall Street and Main Street.
In the wake of the latest monetary policy adjustments, the central bank has initiated a substantial reduction in borrowing rates, often referred to as an interest rate cut. This strategic maneuver aims to enhance affordability for consumers and businesses, alleviating some of the financial pressures stemming from high borrowing costs. As the economy braces for potential growth, analysts are keenly monitoring how these changes will influence credit terms and overall economic expansion. The expectation is that lowering consumer loan rates will ultimately foster increased spending and investment. Stakeholders are particularly attentive to the evolving dynamics of the housing market and the subsequent impacts on fiscal health.
Understanding the Recent Fed Rate Cut
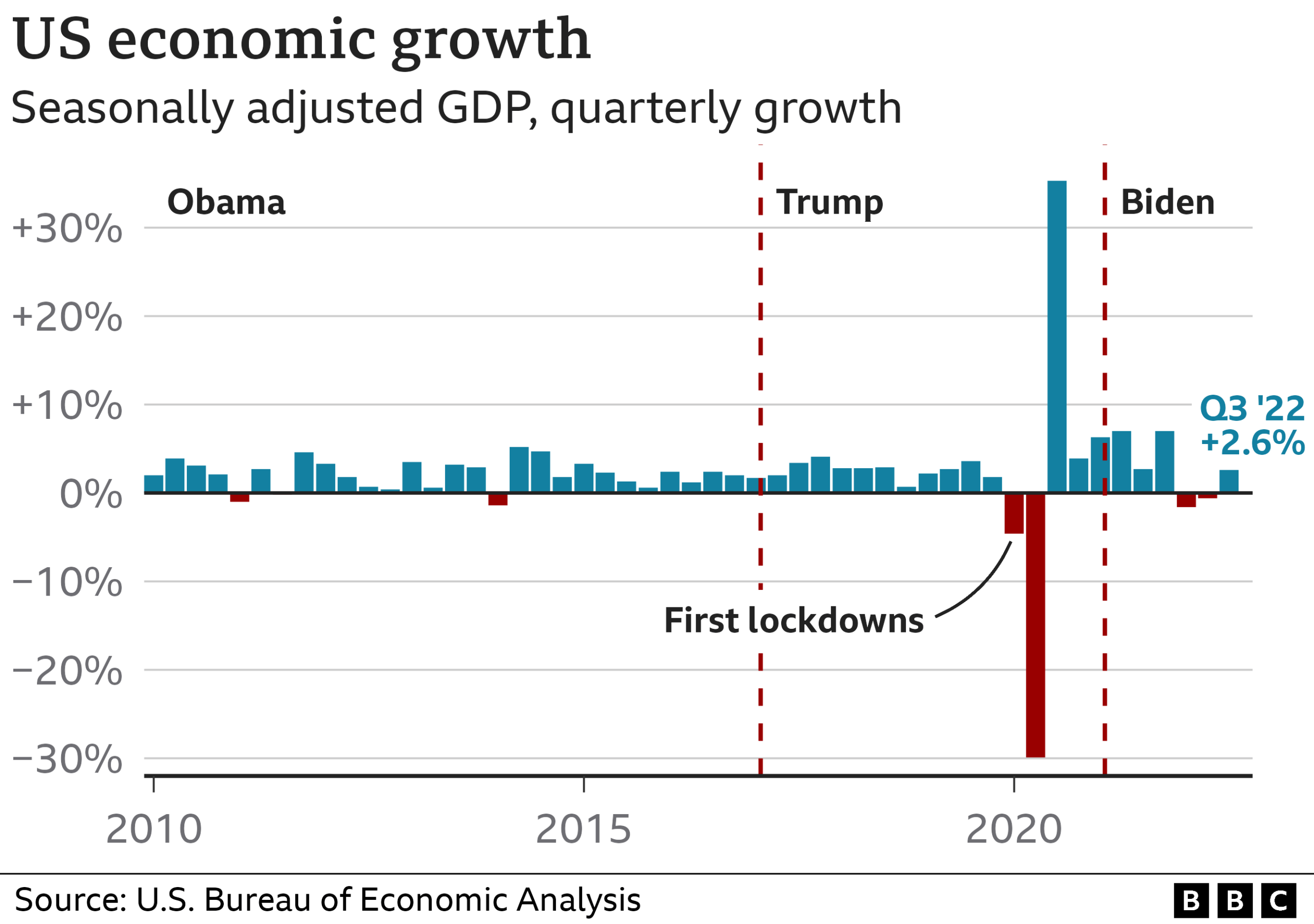
The recent decision by the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates marks a significant shift in monetary policy, aimed at stimulating economic growth. This rate cut, a half percentage point reduction, was larger than anticipated and is expected to have far-reaching effects on various sectors of the economy. Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell highlighted that this strategy is designed to support both consumers and businesses by reducing borrowing costs, enhancing liquidity in the market, and boosting overall economic confidence.
In light of these changes, consumers can expect noticeable benefits, particularly in areas such as credit card debt and mortgage costs. With the Fed’s commitment to potentially lower rates further in the coming months, households may find it easier to manage their financial obligations, leading to increased consumer spending—a key driver of economic growth. However, the ultimate economic impact hinges on how quickly these lower rates translate into tangible benefits for everyday Americans.
Impact of Federal Rate Cuts on Mortgage Rates
Mortgage rates are inherently linked to the Federal Reserve’s decisions on interest rates. As the Fed continues to ease its monetary policy, we anticipate a downward trend in mortgage rates, which could foster improved housing affordability. While current mortgage rates remain relatively high, the expectation of sustained cuts could serve as a catalyst for prospective home buyers who have been hesitant due to financial pressure. Lower mortgage rates can stimulate the housing market, leading to more transactions and ultimately providing further support to the economy.
Moreover, the easing cycle is likely to alleviate some of the affordability challenges that have plagued the real estate market in recent years. As prospective buyers face lower borrowing costs, they may regain confidence in pursuing homeownership. However, it is essential to note that despite these optimistic projections, market realities—such as ongoing supply constraints and rising home prices—could temper the impact of lower mortgage rates on overall housing affordability.
Consumer Borrowing Costs: What to Expect After Fed Rate Cuts
As the Federal Reserve cuts interest rates, consumers are poised to see changes in their borrowing costs, which encompass not only mortgages but also credit cards and personal loans. However, the timeline for these reductions is uncertain, as various factors influence interest rates beyond the Fed’s actions. For instance, lenders consider future economic indicators and individual credit risk when setting rates, meaning that immediate relief may not be felt by all consumers.
Despite this, consumers are likely to experience gradual improvements in borrowing costs over time. The expectation is that by lowering the federal funds rate, the overall cost of lending will decrease, which could encourage more borrowing and, consequently, spending. This could reinvigorate sectors like retail and services, further bolstering the economy. However, the extent and speed of these changes will depend on how quickly lenders adjust their rates in response to the Fed’s cuts.
Long-Term Economic Impacts of Fed Rate Cuts
One of the primary goals of the recent Fed rate cut is to prompt long-term economic growth by stabilizing consumer spending and investment. Lower interest rates typically encourage borrowing and spending, which can help businesses expand and create jobs. In the context of current economic conditions, this strategic maneuver is particularly crucial as it aims to maintain a delicate balance between stimulating the economy while managing inflation.
As the impacts of these rate cuts unfold over the next few months, we can anticipate a modest uptick in economic activity. Increased consumer confidence, resulting from more accessible credit, coupled with a healthier job market, may lead to a gradual yet firm recovery. However, analysts warn that the success of this strategy relies heavily on external economic factors, including inflation trends and geopolitical tensions, which could impede or amplify the effectiveness of the Federal Reserve’s approach.
Preparing for Future Interest Rate Predictions
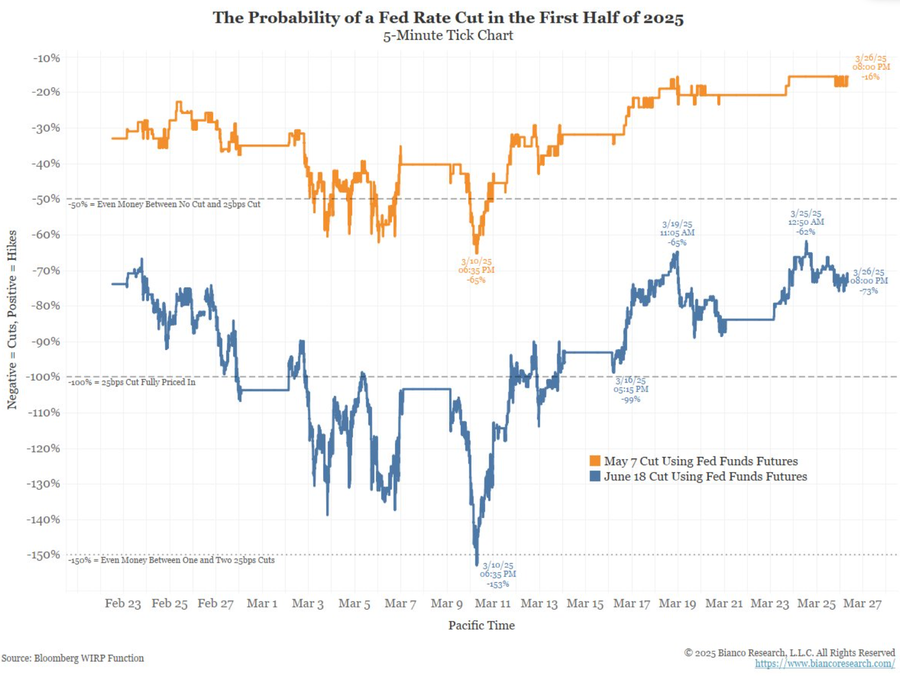
Economic forecasts following a Fed rate cut often involve predicting future interest rate adjustments. Investors and consumers alike watch closely for signals from the Fed regarding upcoming decisions on monetary policy. Rate predictions can swing based on macroeconomic data such as employment figures and inflation trends, making it crucial for stakeholders to stay informed about these variables.
Moreover, financial markets react to the anticipation of future rate changes, which means that rate cuts can lead to fluctuations in stock prices and investor sentiment. The expectation is that if the economy shows signs of strengthening, the Fed may be inclined to reconsider its easing approach, leading to further adjustments in interest rates in the months ahead. Ultimately, vigilance in tracking economic indicators will be essential for navigating the evolving landscape influenced by Federal Reserve policies.
The Role of the Federal Reserve in Consumer Economics
The Federal Reserve plays a pivotal role in shaping consumer economics by adjusting interest rates to align with broader economic objectives. Their policies directly influence the cost of borrowing, thereby affecting consumer behaviors regarding spending, saving, and investment decisions. When the Fed cuts rates, households often feel encouraged to take on new debts, such as mortgages and student loans, which can energize various sectors of the economy.
In essence, the Federal Reserve’s actions create a ripple effect throughout financial markets and consumer psychology. A lower interest rate environment not only incentivizes spending but also instills a sense of economic optimism, prompting consumers to engage more actively in their financial commitments. However, it is essential for individuals to remain cognizant of their financial positions and potential risks, such as increasing debt levels that might arise during a favorable borrowing climate.
Navigating Economic Uncertainty Amid Fed Rate Cuts
In the wake of Fed rate cuts, navigating economic uncertainty becomes vital for consumers and businesses alike. While lower interest rates provide immediate relief in borrowing costs, the long-term implications are influenced by external factors like inflation and market volatility. Consumers must remain agile and informed to adapt to the evolving economic landscape.
Furthermore, businesses might find themselves reassessing their growth strategies in light of the changing borrowing environment. The stakes are high as they aim to capitalize on lower rates for expansion while remaining vigilant against potential risks stemming from economic shifts. Building a robust contingency plan is essential for both consumers and businesses as they prepare to navigate the complexities resultant from the Fed’s monetary policy changes.
Consumer Response to Fed Rate Preemptive Actions
Consumer response to the Federal Reserve’s preemptive rate cuts can significantly influence economic recovery. As the Fed lowers rates, it is expected that consumers will react by increasing spending, particularly on large-ticket items that often rely on favorable financing options. The assumption is that with lower borrowing costs, the appetite for debt will increase, providing a much-needed boost to the economy.
However, consumer sentiment can be unpredictable, and the effectiveness of rate cuts depends heavily on public perception of economic stability and confidence levels. If consumers feel insecure about their financial situations, they may prioritize saving over spending, counteracting the intended effects of the Fed’s actions. Understanding these dynamics will be crucial for policymakers and economists as they gauge the success of rate cuts in stimulating economic activity.
The Future of Monetary Policy in a Post-Cut Economy
Looking ahead, the future of monetary policy in a post-cut economy remains a subject of intense debate among economists and financial experts. The implications of the recent Fed rate cut will likely linger well into the future, influencing subsequent policy decisions as the central bank gauges the economy’s response. As mentioned by Fed Chairman Powell, appropriate recalibration of policy will depend on carefully monitoring economic conditions.
As financial markets adjust to the current interest rate environment, stakeholders will keenly observe how the Fed’s actions shape consumer behavior and overall economic growth. The dialogue surrounding interest rate predictions and monetary policy is far from over, and consumers, businesses, and analysts alike must adapt to ongoing shifts in the economic landscape to make informed financial decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of the Fed rate cut on Federal Reserve interest rates?
The recent Fed rate cut lowers the key Federal Reserve interest rates by half a percentage point, making borrowing cheaper. This is expected to stimulate economic activity by reducing costs for loans, consumer borrowing, and potentially leading to lower mortgage rates.
How will the Fed rate cut affect mortgage rates?
Mortgage rates are likely to decrease following the Fed’s decision to cut rates. As the Federal Reserve eases policy, it reduces borrowing costs, which can lead to more affordable mortgages for homebuyers, improving housing affordability.
What is the economic impact of rate cuts by the Federal Reserve?
The economic impact of Fed rate cuts includes increased job creation and economic growth over time. Lower interest rates encourage consumer spending and investment, which can help stabilize the economy and prevent a recession.
How does the Fed rate cut influence interest rate predictions?
The Fed rate cut influences interest rate predictions by signaling to markets that further cuts may occur, thereby setting expectations for lower future borrowing costs. Traders and financial analysts adjust their forecasts based on the Fed’s actions and guidance.
Will consumers see a decrease in borrowing costs due to the Fed rate cut?
Yes, consumers are expected to see a decrease in borrowing costs, as the Fed rate cut typically leads to lower interest rates on various loans, including car loans and credit cards, easing financial burdens for many borrowers.
How does the Fed rate cut address the housing affordability crisis?
The Fed’s rate cut can address the housing affordability crisis by lowering mortgage rates, which should make buying homes more accessible and affordable for consumers. However, the extent of this impact also depends on broader economic factors.
Is the Fed rate cut a response to economic conditions?
Yes, the Fed rate cut is a response to current economic conditions, particularly to reduce inflationary pressures while supporting growth. The central bank uses rate cuts to manage the economy and respond to labor market changes.
How long will it take for consumers to feel the effects of the Fed rate cut?
While the Fed rate cut has an immediate impact on markets, it may take several months for consumers to feel significant relief in borrowing costs. Economic adjustments to lower rates can vary based on existing debt and market conditions.
What potential future actions might the Fed take after this rate cut?
Following this rate cut, the Fed may implement additional cuts if economic conditions warrant. Initial forecasts suggest that two more cuts could occur within the year, depending on inflation reports and labor market performance.
How does consumer debt repayment relate to the Fed rate cut?
Consumer debt repayment may ease slightly due to lower interest charges following the Fed rate cut, but current debt levels and market expectations still influence the rates consumers face, leading to a gradual decrease in repayment burdens.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Fed cut interest rates by 0.5 percentage points, the first cut in four years. |
| Chairman Powell sees potential for further cuts, possibly another two by the end of the year. |
| The rate cut is expected to benefit consumers with credit card debt, car loans, and mortgages. |
| Impact on job creation and economic growth anticipated in the next 6-12 months. |
| Mortgage rates expected to decline further as the Fed continues its easing policy. |
| Consumer relief from high interest rates may take time, with uncertainty remaining. |
Summary
The recent Fed rate cut signifies a pivotal moment in the economic landscape, as it aims to alleviate borrowing costs for consumers. While the immediate effects may take time to manifest, the Fed’s move is intended to foster economic stability and support the labor market. As the Fed considers potential further cuts, both consumers and businesses alike are encouraged to remain cautious yet optimistic about the economic recovery fueled by these decisions.